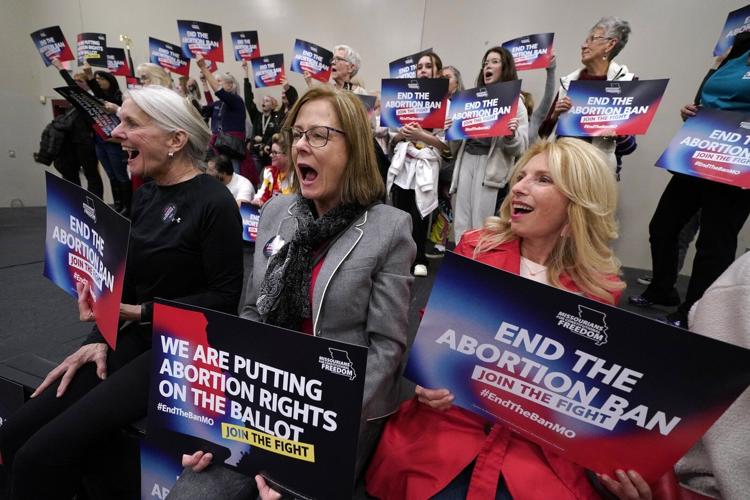
KANSAS CITY, Mo. (AP) ÔÇö Abortion-rights advocates are asking a judge Wednesday to overturn MissouriÔÇÖs near-total ban on the procedure, less than a month after voters backed an abortion-rights constitutional amendment.
Jackson County Circuit Judge Jerri Zhang was set to hear arguments from Planned Parenthood and the stateÔÇÖs Republican Attorney GeneralÔÇÖs Office over whether to issue a temporary order blocking enforcement of MissouriÔÇÖs numerous abortion laws.
ÔÇťIf left in place, the above-described restrictions will continue to be catastrophic for Missourians," lawyers for abortion-rights supporters wrote in a court brief. "They will either prevent care altogether or severely delay or interfere with care.ÔÇŁ
Missouri is one of this year to add the right to an abortion to their state constitutions. Nevada voters also approved an amendment, but theyÔÇÖll need to pass it again in 2026 for it to take effect. Another that bans discrimination on the basis of ÔÇťpregnancy outcomesÔÇŁ prevailed in New York.
Reproductive rights advocates in Arizona on Tuesday a 15-week abortion ban that conflicts with that state's new constitutional amendment expanding access up to fetal viability.
The Missouri amendment does not specifically override any state laws. Instead the measure leaves it to advocates to ask courts to knock down bans that they believe would now be unconstitutional.
Missouri Attorney General Andrew Bailey, an abortion opponent, last week issued agreeing that most abortions will be legal when the amendment takes effect Thursday.
But BaileyÔÇÖs office is still fighting for a ban on most abortions after viability, along with a number of regulations that Planned Parenthood argues made it nearly impossible to offer abortions in the state even before abortion was almost completely banned in 2022.
MissouriÔÇÖs constitutional amendment allows lawmakers to restrict abortion after viability, with exceptions to ÔÇťprotect the life or physical or mental health of the pregnant person.ÔÇŁ
The term ÔÇťviabilityÔÇŁ is used by health care providers to describe whether a pregnancy is expected to continue developing normally or whether a fetus might survive outside the uterus. Though thereÔÇÖs no defined time frame, doctors say it is sometime after the of pregnancy.
Other abortion laws that Bailey is defending include a 72-hour waiting period before an abortion can be performed; bans on abortions based on race, sex or a possible Down syndrome diagnosis; and a requirement that medical facilities that provide abortions be licensed as ambulatory surgical centers.
The Attorney General's Office argued that Planned Parenthood has not proven it will be negatively impacted by those laws, noting that no abortions have been scheduled yet.
ÔÇťPlanned Parenthood concedes they have no appointments scheduled for right after the amendment goes into effect and have not even tried to obtain relevant licenses or create necessary complication plans," state attorneys wrote in a court brief.
It is unclear when Zhang will rule on the request for a preliminary injunction.